On July 25, 2025, Carbonstop hosted an extraordinary industry summit in Beijing—the 2025 GCMC Global Carbon Management Conference·China Carbon Management Forum—and released the "Ten Insights on the Global Carbon Management Industry: Five Years of Dual Carbon Goals."
The theme of this conference was"Breaking Boundaries·Reshaping: New Momentum for Enterprises," inviting representatives from over a hundred leading enterprises and institutions, including CNCA, MIIT, China Customs, Beijing Municipal Ecology and Environment Bureau, WRI, MSCI, WWF, Beijing Economic-Technological Development Area, Suzhou Industrial Park, Lenovo, LONGi, BAIC, Meijin, ZhenGu, Baidu, Mixue Bingcheng, Mengniu, Ant Group, Yili, Starbucks, Perfect World, Bloomage Biotechnology, CICC, Hello, Oriental Cable, BOE, Bank of Beijing, China Unicom, China Telecom, State Energy Group, CGN, Sinopec, China Knitting Industry Association, Goldwind, Asymchem, Shennam Group, Second Tree, EQT, and Frost & Sullivan,to jointly discuss global trends, technological innovations, and corporate practices in the field of carbon management, injecting wisdom and momentum into advancing China's "dual carbon" goals.
The GCMC venue was selected at the Horticultural Innovation Center of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, a "treasure" conference location full of greenery and sustainability elements. Since the venue is inside a greenhouse, it perfectly echoes our original intention of discussing with all guests how to mitigate the greenhouse effect and explore the right pathways for addressing climate change. The venue is exceptionally beautiful; in the future, if carbon community partners need to host a sustainability-related industry summit in Beijing, you can choose this place(free advertisement)—it definitely won't disappoint!
The conference opened with a speech by Erik Solheim, former UN Under-Secretary-General, who expressed his appreciation for China's achievements in environmental pollution prevention and climate change response in recent years, and also stated thatfighting carbon emissions is the core battlefield of green transformation. As an industry pioneer, Carbonstop has taken the lead in driving corporate green transformation with an artificial intelligence engine, and its innovative practices are profoundly significant.
After Erik's speech, People.cn also published his remarks and praise for China's "dual carbon" achievements.
Image source: Screenshot from People.cn
This is the second time we have hosted the GCMC Global Carbon Management Conference (the last one was in 2022). Every time standing on the GCMC stage, I feel incredibly excited and nervous inside, because every time we present the industry's top ten insights, it is a process of accumulation, organization, distillation, and elevation, and we also hope to share our thoughts and observations on the industry.
This year marks the fifth anniversary of China's proposal of the dual carbon goals and the tenth anniversary of the Paris Climate Conference. The GCMC Global Carbon Management Conference·China Carbon Management Forum is rooted in China while looking at the world, grounded in the present while looking towards the future. Looking back on the past five years of dual carbon goals, many significant changes and milestone events have occurred in China's carbon management market. This sharing is also a presentation from the industry perspective and from the standpoint of entrepreneurs deeply involved in the field, offering our "Ten Insights on the Global Carbon Management Industry: Five Years of Dual Carbon Goals."
First Insight: Moving Against the Tide, Five Years of Dual Carbon Goals—China's Carbon Management Firmly Enters the Fast Lane!
In today's environment filled with countless uncertainties, people may feel that "dual carbon" is not as hot as it was in previous years. As a professional carbon management organization in the industry, we still see many different aspects and hope to share them one by one.
Firstly, regarding the global climate, the global average temperature in 2024 has already exceeded 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels (1.55 ± 0.13 °C), and our long-held temperature rise target is now precarious. On July 22, 2024, the world experienced its hottest day, with the global average temperature reaching 17.16°C. The day before the conference, July 24, 2025, was also this year's Earth Overshoot Day, meaning that from that day onward, we began to overdraw Earth's resources. Earth Overshoot Day usually falls around August 1; this year it came 5 to 6 days earlier.
From an international perspective, over the past five years, global climate governance has experienced many uncertainties and fluctuations, including the United States' withdrawal from the Paris Agreement (when we chatted with executives from our American counterpart Watershed last month, they mentioned their company is now counting down every day to the next presidential transition), and Europe's "reduced effort" Omnibus bill, which made major compliance policies such as CSRD, CSDDD, and CBAM seem like much sound and little fury. But looking at the past five years as a whole, we conducted a comparative analysis using data from the four most influential corporate carbon management disclosure platforms and rating agencies, and found the results are not entirely as most of us imagined.
As can be seen from the chart above, all four global organizations have experienced at least a doubling in growth, especially the number of Chinese enterprises committing to SBTi, which is 100 times higher than five years ago. The number of enterprises included in EcoVadis globally has exceeded 160,000, and the number of Chinese enterprises participating in EcoVadis disclosures has surpassed 20,000. This fully demonstrates the remarkable development of global enterprises in carbon management and disclosure.
In the past five years, "dual carbon" has consistently been a key national policy highlighted in the government work reports at China's annual "Two Sessions," and it has become increasingly detailed in specific tasks. For example, in 2024, it was explicitly stated to establish a carbon footprint management system; in 2025, the national carbon market will expand its industry coverage, establish a number of zero-carbon parks and zero-carbon factories, and set up a product carbon footprint management system and carbon label certification system.
Returning to the enterprise side, starting in 2020, companies have gradually made carbon neutrality commitments, with most promising to achieve carbon neutrality around 2030, and some more proactive companies aiming for 2025. Previously, these goals seemed far off, but now it is already 2025, and the time has come to fulfill these carbon neutrality commitments. Therefore, companies are now closely focusing on how to reduce emissions and how to invest in purchasing high-quality carbon credits, which will become the driving force for the entire industry's advancement.
In summary, carbon neutrality remains a social hotspot and the greatest challenge facing the globe (perhaps without exception), carbon neutrality remains a very certain card for China's future over the next 30+ years, and carbon neutrality will undoubtedly be an epic-level super golden track worth trillions.
Since the proposal of the dual carbon goals, carbon management has developed over five years (some leading enterprises have even practiced carbon management for nearly 20 years; for example, Lenovo published its first carbon inventory report in 2008). More and more enterprises have established basic carbon accounting capabilities, and a significant proportion of these enterprises have built their own digital platforms, as if they are all beginning to explore new journeys.
Second Insight: Carbon Management Enters the Second Half—Advanced Carbon Management!
For carbon management, we define its first half as "compliance," which includes compliance operations such as product carbon, organizational carbon, CDP, EcoVadis, ESG reporting, CBAM, and the battery regulation, primarily driven by downstream customer demands or policy requirements; whereas entering the second half of carbon management, a significant characteristic is "value creation," including opportunities for new customer orders, investment returns, and consumer recognition.
In the first half, we often said"Without quantification, there is no management"; while in the second half, a major characteristic we define is"Without advanced carbon management, there is no carbon neutrality." The capabilities and tools required for advanced carbon management are completely different from those in the first half. We need to manage Scope 3 more deeply, extensively explore emission reduction opportunities, drive supply chain emission reductions, establish internal carbon pricing mechanisms, engage employees and users in emission reduction actions, select high-quality carbon credits, and conduct scientific and efficient communication, which have become the current challenges and difficulties for most enterprises.
First, let's introduce the first component of advanced carbon management: Scope 3, which we both love and hate.
Many enterprises have already addressed Scope 1 and 2, and perhaps even attempted simple categories of Scope 3 (such as purchased goods, business travel, employee commuting, etc.), but when companies need to submit to SBTi or fully disclose Scope 3, they encounter numerous challenges. Many exchanges (e.g., HKEX) have also imposed mandatory disclosure requirements for Scope 3, making Scope 3 the top priority for advanced carbon management in enterprises.
From last October to now, I have been actively participating in the GHG Protocol Scope 3 working group discussions, having in-depth exchanges with some leading international carbon accounting peers on carbon management and Scope 3, gaining many insights and reflections. To address the challenges most enterprises currently face with Scope 3, we are officially establishing a Scope 3 Study Society in China, aiming to enhance the overall capability of Chinese enterprises in managing Scope 3. We will organize several online and offline courses, combining insights from Carbonstop's Scope 3 experts with top international and domestic Scope 3 experts, and inviting leaders from leading enterprises in Scope 3 carbon management to share their practical experiences. The QR code below leads to the Scope 3 Study Society group; partners who wish to delve into the field of Scope 3 are welcome to scan and join.

At 3 PM on August 15, the first Scope 3 class: How to Audit the Carbon Footprint of Purchased Goods? Focusing on Category 1 & 2 of Scope 3, interested participants can scan the code to register!

Carbon management entering the second half is not only because business maturity has entered the second half, but also because technological innovation has entered the second half. More advanced tools, including AI, software, databases, and other technologies gradually maturing, make it more realistic for enterprises to conduct advanced carbon management.
From product carbon footprint, organizational carbon accounting to online certification; from data benchmarking to emission reduction, and then to investment and procurement of high-quality carbon credits; from carbon accounts to supply chain carbon management; from CBAM, CDP to ESG reporting, enterprises can only maintain an advantage or achieve a turnaround in the second half of carbon management by establishing comprehensive carbon management capabilities, leveraging technological innovation, and utilizing the support of partners!
Speaking of technological innovation, AI waves have surged one after another in the past two years, large models have swept the globe, and ChatGPT, DeepSeek constantly amaze and impress everyone, as if the entire world is being redefined by AI.
Last month, I attended a CEO summit hosted by Sequoia, which was directly named Sequoia AI Day (the theme was AI Agent: From Copilot to Colleague). The emergence of Agents represents the biggest change in AI—transitioning from a tool to a "partner,"evolving from "machines as human assistants" to "humans as machine assistants." What can AI actually bring us? I believe there are two levels of value:
- Improving efficiency. All AI tools are freeing people from simple, repetitive, and labor-intensive tasks, allowing Agents to replace humans, significantly improving efficiency while greatly reducing costs;
- Surpassing cognition. A common saying is that cognition is the greatest competitive advantage. The emergence of AI Agents can turn work that people previously couldn't do or even imagine into reality. A partner from Sequoia shared a case: when he asked Zhang Yiming from ByteDance about the logic behind product design and why intelligent recommendations were used instead of letting users specify what information/videos they wanted to see, Zhang Yiming replied: "I bet I understand the user better than the user himself." Now that Agents have emerged, in various industries and fields, it's possible to create functions or applications that people couldn't imagine before, which is the part that surpasses human cognition, and this is what I believe to be the greatest value of AI.

In the global carbon management market, AI is also a new weapon, perhaps even anuclear weapon, and carbon accounting and carbon management will be redefined by AI.


Third Insight: AI Agent, Defining the Next Generation of Carbon Management!
In today's era, every enterprise deserves to have its own carbon management intelligent agent, and carbon management will become unprecedentedly intelligent and efficient. AI Agents have now matured in many fields. In the field of carbon management, many leading carbon management platform companies are also exploring,the simple, repetitive, and labor-intensive work of carbon consultants will gradually be taken over and absorbed by Agents, while high-value carbon consultants should focus on advanced carbon management, continuously exploring the unknown.
In this Agent era, Carbonstop globally launched its carbon management Agent—Carbon AI Agent—at the conference. Carbon AI Agent is built upon 14 years of Carbonstop's accumulation from thousands of projects, nearly ten thousand product carbon footprint models, and hundreds of thousands of enterprise carbon data points. Based on this Agent, capabilities such as AI data collection, automatic modeling, matching emission factors, AI emission reduction strategies and asset allocation, AI CDP pre-scoring, and AI-generated ESG reports can be achieved, forming a "data analysis → accounting modeling → emission reduction actions → compliance disclosure" closed loop,reducing traditional carbon management's reliance on manual labor by 70%, allowing enterprises to focus on strategic decision-making rather than data operations.

Global debut of Carbon AI Agent
At the conference, we demonstrated all the above functions to all offline and online guests, winning enthusiastic applause.
(Carbon AI Agent performing product carbon footprint modeling)

(Carbon AI Agent providing scientific emission reduction recommendations and cost analysis for product carbon footprint projects)
(AI Agent conducting pre-scoring of CDP questionnaires and providing reasonable suggestions for score improvement)
At the same time, we conducted a comparison with leading international peers (mostly service providers listed in Gartner's global carbon management platform recommendations), and as shown in the figure below, Carbon AI Agent currently leads comprehensively across the entire spectrum of carbon management. These achievements are hard-earned, and Carbonstop will continue to adhere to the principle of technology-driven innovation, striving to be at the forefront of technological advancements in carbon management!

Functional comparison of Carbon AI Agent with major global carbon management Agents
If you are interested in Carbon AI Agent, please click here to leave your information, and we will arrange for an expert to provide you with a product demonstration.


Fourth Insight: China's Carbon Data is Becoming a Crucial Foundation for Global Carbon Neutrality.
As the global carbon neutrality process deepens, the demand for corporate carbon management is becoming increasingly rigid and intense, making Scope 3 and supplier-specific real-world data particularly valuable. In the process of carbon calculation, the value of enterprise-specific real-world data far exceeds that of background data, and China is precisely the largest source of such real-world data. In recent years, governments at all levels, associations, universities, and enterprises have actively joined the construction of carbon databases. China's local carbon data has become a gold mine that all institutions are eager to explore, serving as a solid cornerstone for advancing global carbon neutrality.
Regarding carbon databases, let's first discuss our understanding: their core goal is to help enterprises and organizations across various industries independently conduct carbon calculations and provide a data foundation and decision-making basis for carbon reduction and carbon neutrality. We have categorized carbon data as follows:
The most discussed iscarbon factor data, which is the foundation of carbon calculation. Globally, there has been a surge in creating and generating carbon factor data in recent years (used for calculating product carbon footprints and organizational carbon accounting), including ILCD format (or internationally standardized LCA data) and non-ILCD format data (such as factor result data released by governments or authoritative institutions, EEIO data, etc.);
The second level of carbon databases isenterprise carbon data, which is also the scarcest and most valuable real-world enterprise data. It includes enterprise Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions data, product carbon footprint data, and product carbon reduction data, all of which are the foundation for guiding enterprises in carbon reduction.
The third level of carbon databases ishistorical data. This type of data is often overlooked by enterprises or consulting firms, but it is now found to have significant utility, such as when calculating historical carbon emissions or tracing product carbon reduction performance, where historical data is frequently required.
The fourth category of data in carbon databases we define asbehavioral data, which has not been extensively explored yet but will play an increasingly important role. This data primarily consists of user behavior data from carbon management platforms, such as the frequency of selecting emission factors, which can determine the quality and priority of emission factors, proving highly practical in enterprise carbon accounting and management. In actual enterprise carbon management, we don't just want a long list of carbon data; instead, we need guidance on which carbon data to use in specific scenarios, which is the most valuable aspect—yet often missing in current databases.

Based on the above understanding, we are now upgrading CCDB from a purely Chinese carbon factor database to aChinese Carbon Database, incorporating carbon factor data and enterprise real-world carbon data, amplifying the value of CCDB to better serve enterprises and organizations across various industries.

Carbonstop began building its carbon database in 2012, and in 2022, we announced at our first GCMC conference that our CCDB had reached 150,000 data entries, committed to becoming a leading carbon factor database in China and globally, covering over 200 countries and regions worldwide, as well as data from dozens of key industries.

Today, we officially announce that CCDB's data volume has achieved several-fold growth, reaching 512,432 entries, with over 300,000 carbon factor data entries and over 200,000 enterprise carbon data entries; data from China exceeds 200,000 entries, accounting for about 40%; real-world data reaches 220,000 entries, accounting for over 43%. Over the past five years and in the coming decades, Chinese data and real-world data will remain key development directions for CCDB, and CCDB has become the core and foundation for Carbonstop's development of AI Agents. We hope to fully unleash the capabilities of CCDB and AI Agents to provide maximum support for enterprises on their journey of carbon management and carbon neutrality.

As mentioned earlier, governments, industry associations, and enterprises are all building carbon databases. While this is positive and vibrant, it indeed leads to significant redundant construction and resource waste. I am often asked about the respective roles each stakeholder should play in carbon database development. I believe that national governments possess the most core and abundant statistical data; therefore, national-level foundational energy and basic materials databases should be built by government departments, forming the foundation of the carbon database. Industry associations and organizations, due to their know-how in specific industries, should develop industry-specific carbon databases, serving as the branches of the carbon database. With the vast number of enterprises, each enterprise or third-party institution's carbon database generated during carbon accounting is closer to an application-level database. All parties should collaborate to advance progress, while focusing on international recognition and cooperation, making the value of China's carbon databases increasingly significant, undoubtedly becoming a crucial cornerstone for advancing global carbon neutrality.


Fifth Insight: Carbon Footprint is Becoming the New Standard for Consumption!
Although low-carbon consumption has been continuously关注ed in recent years, the overall situation is still lukewarm and has not reached the expected height. Companies are constantly reducing the premium of low-carbon products, and consumers are constantly accepting the premium of low-carbon products, which are advancing simultaneously. There is still a distance between the intersection of the two. We predict that this intersection will accelerate with the successive introduction of strong international and domestic low-carbon policies.
China has made product carbon footprint a core driver for promoting China's carbon neutrality and ensuring the competitiveness of Chinese enterprises in the international market. The whole society's attention to carbon footprint and carbon labeling has reached an unprecedented height. The latest survey report from the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences also shows that 60% of respondents are willing to pay a premium for low-carbon products, and we believe this proportion will continue to increase.
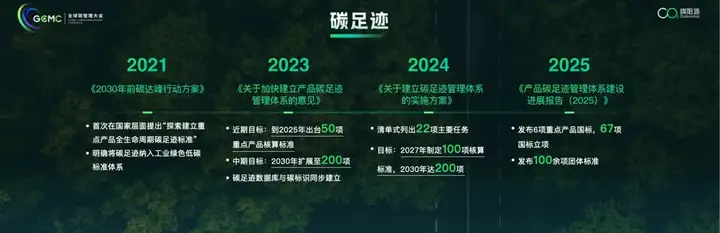
The China Carbon Label released by the National Certification and Accreditation Administration (CNCA) at the beginning of this year has the opportunity to become a new and perhaps the biggest driving force for enterprises to carry out carbon footprint management.
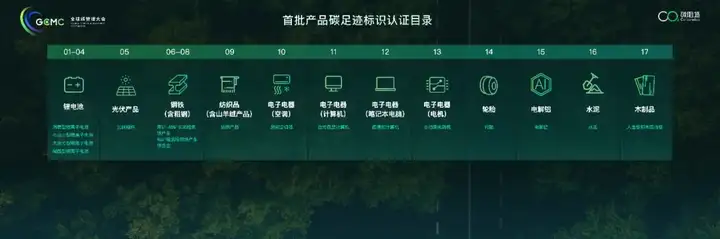
CNCA's First Batch of Product Carbon Footprint Label Certification Catalog
Enterprises that obtain the national carbon label will receive more priority in government procurement, and will also have a huge positive impact on consumers' minds. In the future, it may become as deeply rooted in people's hearts as the energy efficiency rating of household appliances. According to internal information, the impact of the carbon label may be far greater than the energy efficiency rating, so this is very much worth looking forward to.


Sixth Insight: The Deep Water Zone of Corporate Carbon Management - Supply Chain Carbon Management
As mentioned earlier, real-world data is the foundation of scientific carbon management for enterprises, and data from suppliers is the core source of real-world data. Whether it is product carbon footprint or Scope 3 of organizational carbon accounting, it is inseparable from high-quality real-world data from suppliers. How to efficiently collect high-quality data from suppliers, how to improve the carbon management level of suppliers, and how to develop collaboratively with suppliers in the field of sustainability are currently becoming the core content of advanced carbon management for many enterprises!
Recently, the Carbonstop team, under this big background, with the attitude and mission of solving practical problems for enterprises, and combined with the experience accumulated in many carbon footprint projects and Scope 3 inventory projects regarding supply chain carbon management, developed and produced the "2025 Supply Chain Carbon Management White Paper", hoping to provide some reference and assistance to enterprises facing supply chain carbon management challenges!
Regarding supply chain carbon management, first share a concept:Supplier Readiness. In the process of doing Scope 3 or product carbon footprint projects, companies often face a choice: whether to use background databases or real-world data from suppliers. In most scenarios, we will not hesitate to say, of course, choose real-world data from suppliers. This is correct, but not entirely correct. In a GHG Protocol Scope 3 expert meeting, a few experts pointed out that obtaining data from suppliers is certainly a good thing, but in actual projects, when tracing back to T2 and T3 suppliers, the data quality is often not high or the cooperation of suppliers is not high, which greatly reduces the quality of real-world data. However, continuously improving the data quality of suppliers is the goal we need to pursue, so we believe that making the supply chain ready for carbon management is an important way for enterprises to achieve carbon management and carbon neutrality."Supplier Readiness" is also the first and most important step for enterprises in various industries to promote supply chain carbon management.

The most core release of the "2025 Supply Chain Carbon Management White Paper" is the supply chain carbon management methodology:MERIT. This methodology is based on theclosed-loop logic of "Measure - Engage - Reduce - Invest - Trace" as the core, building a full-link management system from carbon quantification to value creation.
With the tightening of global climate policies, the acceleration of technological iteration, and the upgrading of market demand, supply chain carbon management is transforming from "compliance-driven" to "value creation", presenting the following three trends:
- From "mandatory compliance" to "proactive leadership", reconstruct corporate industrial competitiveness;
- Deep integration of digitalization and collaboration, reshaping the supply chain ecosystem;
- Carbon finance tools activate the potential for supply chain emission reduction, creating new business models and market value.

The report also shares best practices in supply chain carbon management from many leading companies around the world. For more information about the white paper, pleaseclick here, welcome to download!


Seventh Insight: Personal Carbon Accounts - A Standard Configuration for Advanced Corporate Carbon Management
In the CREOS carbon neutrality methodology, Engaging has always been the focus of enterprises to carry out in-depth carbon management. In addition to how to drive the supply chain to carry out carbon management, as discussed in the previous chapter, another very important content is to drive employees and consumers to participate in carbon reduction actions together.
With the vigorous promotion of carbon inclusion and carbon accounts by governments at all levels and enterprises in various industries in recent years,personal carbon accounts have become a standard configuration for advanced corporate carbon management!
We divide personal carbon accounts into three categories: government-side carbon inclusion for citizens, enterprise-side carbon accounts for employees, and enterprise-side carbon accounts for consumers.
The following is an analysis of the carbon inclusion market across the country that we have compiled. Guangdong, Beijing, Shanghai, Chengdu, Wuhan and other places are at the forefront of the country in carbon inclusion work, and have also achieved fruitful results, such as:
- Guangdong Carbon Inclusion is the first carbon inclusion market in the country, currently covering 6 carbon inclusion methodologies, with a total carbon emission reduction of more than 2.47 million tons, affecting 420,000 people;
- Beijing Carbon Inclusion focuses on green travel, releasing 3 carbon inclusion methodologies, with a total carbon reduction of 400,000 tons, driving 5.6 million people to participate in carbon reduction actions;
- Shanghai Carbon Inclusion relies on the Shanghai citizen application "Suishenban", releasing 7 methodologies. The trial period of nearly 8 months has attracted the participation of more than 100,000 citizens, with a cumulative transaction of more than 40,000 tons of carbon emission reductions.

We believe that more and more governments will continue to innovate in the carbon inclusion market, allowing more local citizens to actively participate in carbon reduction actions,making green and low-carbon a new calling card for urban development!
Returning to the enterprise side, carbon accounts are divided into employee carbon accounts and consumer carbon accounts. The following are some outstanding enterprise representatives in the field of personal carbon accounts, among which Vipshop, LVMH, and Xiaomi are all carbon account platforms for employees, while China UnionPay and Postal Savings Bank of China's carbon accounts are for all users/consumers. It can be seen that each company has its own characteristics in terms of carbon account design, gameplay creativity, and exchange incentives.

For a company to establish a personal carbon account, the three most critical issues to address are: rich scenarios, creative gameplay, and attractive incentives.
At the conference, we focused on sharing how to enrich the scenarios of carbon accounts. We believe that the first step is to explore quantifiable and actionable carbon reduction scenarios within the company, such as walking and turning off lights. It is also necessary to connect with external scenarios, which is an important way to enrich carbon reduction scenarios. The following figure lists some very common and highly influential carbon reduction scenarios, such as AiHuiShou, Duozhuayu, Too Good To Go, and Feimayi. Each scenario has published its carbon reduction values. Connecting these carbon reduction scenario partners is of great value to companies building carbon accounts and will surely achieve a win-win situation for all parties!
Another area that attracted special attention at the conference was the exhibition area of the Low-Carbon Hero Mall. Finding interesting products with low-carbon attributes is a difficult challenge for most companies building carbon accounts, and Low-Carbon Hero is an ideal place to go.

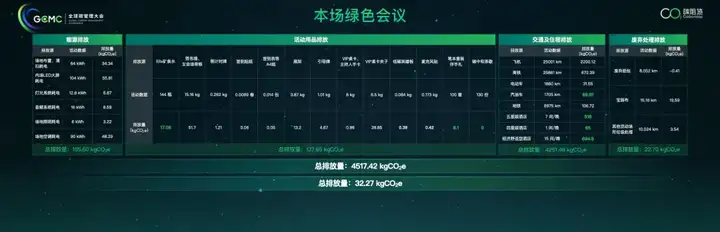
As usual, Carbonstop's conference will be held as a green and carbon-neutral conference. Therefore, we calculated the carbon emissions of the conference from various perspectives and took green and low-carbon measures in many areas to reduce the carbon footprint, such as changing plastic bottled water to paper-packaged water from Finepack, encouraging all guests to travel in a low-carbon way, reusing Logo signs, using low-carbon souvenirs, and zero-carbon refreshments. We are doing our best to help the conference achieve carbon neutrality and influence all participants and the people around them through the conference.
At the carbon neutrality ceremony, all the speakers reviewed the CO2 gesture exercise invented by Carbonstop, which aims to make carbon footprint and carbon reduction more interesting and deeply rooted in people's hearts. The on-site effect was very good, welcome to refer to and "copy"!



Eighth Insight: High-Quality Carbon Credits are Key to Safe Landing for Corporate Carbon Neutrality
In recent years, public opinion has been fluctuating regarding whether companies can choose carbon credits to achieve carbon neutrality. "Greenwashing" and other issues caused by low-quality carbon credits (questionable project authenticity, insufficient additionality, double counting, etc.) have made companies hesitant about carbon credits. However, since this year, with major technology giants purchasing large quantities of high-quality carbon credits, and European countries, known for their strictness, incorporating carbon credits into offset mechanisms, the carbon credit market seems to be ushering in a new round of spring. High-quality carbon credits have become the key to safe landing for corporate carbon neutrality.
The conference shared the layout of leading global companies in investing in carbon credits, such as ByteDance's recent purchase of 100,000 tons of Rubicon's RCT carbon credits, which has caused a stir in the industry; Microsoft's cooperation with Rubicon Carbon to purchase 18 million tons of high-quality carbon credits over the next 15-20 years, covering all ARR projects.

Based on the practical experience and accumulation of Carbonstop's carbon credit development and trading team for many years, we officially released our second important report at the GCMC conference: "High-Quality Carbon Credit Investment Guide" (referred to as the "Guide", welcome to download). The Guide clarifies the standard for high-quality carbon credits, from traditional carbon credits to high-quality carbon credits, and proposes core concerns and standards for the most popular high-quality carbon removal.

Although high-quality carbon credits are favored by the market, they still face a series of problems and challenges such as environmental integrity and credit quality risks, market mechanisms and regulatory differences, technical and execution barriers, and investment-side risks. For investors in high-quality carbon credits, it is necessary to have keen market insight and accurately identify and judge high-quality projects that meet high-quality standards. Through in-depth research and scientific evaluation, it is possible to capture "green gold" in this emerging field and achieve a win-win situation for the environment and the economy.
Carbonstop suggests that investors should carefully consider the following four aspects::
- Strengthen quality screening and establish a standardized evaluation system;
- Promote diversification of investment portfolios to reduce the risks brought about by reliance on a single path;
- Encourage technological innovation to improve the verifiability and long-term nature of carbon credits;
- Strengthen the participation of professional institutions, conduct in-depth analysis and interpretation of the policies, market rules, and methodologies of high-quality carbon credits, conduct detailed project quality due diligence and evaluation, and ensure the smooth issuance of high-quality carbon credits.

As a professional carbon management company with 14 years of experience in the field of carbon management, Carbonstop solemnly launched Carbonstop's high-quality carbon credit portfolio product CCT (Carbonstop Carbon Tonne) at the GCMC conference. CCT meets Carbonstop's high-quality carbon credit standards and is composed of high-quality projects with different mechanisms, project types, and methodologies from international and domestic sources. The Carbonstop team strictly controls project quality and conducts prudent due diligence to ensure that every ton of CCT has authenticity, accuracy, additionality, permanence, traceability, no double counting, and multiple social and environmental benefits, helping customers reduce carbon credit procurement risks and meet the carbon credit quality needs of different carbon-neutral target customers.
The number of companies with high-quality carbon credit procurement and investment needs is increasing day by day. Carbonstop has a natural advantage in obtaining the needs of corporate customers (with more than 1,000 corporate customers who have carbon accounting and have committed to carbon-neutral goals). We also hope to work with many peers in the next few years to develop and invest in high-quality carbon credits and be a connector between the demand side and the supply side of high-quality carbon credits. We also look forward to building a healthy ecosystem with everyone and letting China's high-quality carbon credits win more recognition and applause from the world!


Ninth Insight: Forget Going Abroad, Be Global From Birth!
Everyone has been saying in the past two years: If you don't go abroad, you're out of the game.Domestic involution is becoming increasingly serious. Chinese companies' technology and management levels can be fully utilized on a larger global stage, making going global an essential option for many companies. However, going global itself also faces many challenges, such as understanding local policies and controlling compliance risks. The same applies to the low-carbon field. Whether it's carbon footprint certification, CBAM reporting, or supply chain data disclosure, they all bring professional and cost challenges to companies going global.
As a company based in China and oriented towards the world, Carbonstop provides one-stop services to help companies go global, hoping to ensure that low-carbon aspects at least do not become an obstacle for companies going global, but instead become an aid! So we want to change the very classic slogan "Go global or go out of business" to:Forget going global, born global!I hope that when all our companies face the choice of going global, they can "forget going global" and "be born global" with the support and companionship of Carbonstop!
We also want to share a story of Carbonstop going global itself. Control Risks is a leading global risk consultancy with dozens of branches around the world. In early 2024, Control Risks invited Carbonstop's carbon cloud platform to participate in the bidding project for their global carbon management platform construction. We were quite surprised at the time (we later learned that they knew about Carbonstop because we were the only Chinese company shortlisted in Gartner's list of recommended leading global carbon management platform service providers), but we were also quite hesitant. Firstly, the competition would be very fierce, with top global competitors from the United States, France, the United Kingdom, Germany, etc.; secondly, our international products were not particularly ready. However, after discussing with a group of passionate colleagues and partners, we decided to take a chance and participate in the bidding. The final result was of course good, a pure SaaS order of over £100,000. This is a great incentive for Carbonstop, and also a good case for Chinese companies going global. Talking about this story still makes us feel excited! We have also summarized a few reasons why we won:
- Product strength itself: Carbon Cloud's simple and friendly operating experience and the ability to integrate AI were key to Carbonstop's success;
- Chinese local data: Since Control Risks is a global company, a lot of carbon footprint calculation data requires Chinese local emission factor data. CCDB made a great contribution, letting the other party see that CCDB already has a lot of carbon emission factor data released by China, which made them feel very confident;
- Solving data security issues: We are very grateful to the Amazon AWS team for their timely appearance, which helped us solve many security and data compliance risks encountered when going global;
- Extreme cost-effectiveness: Although Chinese companies often win in cost-effectiveness when going global, this order was not the lowest price.

Since then, Carbonstop has begun to fully blossom in globalization, gaining customers and partners in different countries including the United Kingdom, Spain, France, and Vietnam. They have all established in-depth connections and cooperation with the carbon cloud platform, which has also helped the carbon cloud significantly improve the experience of international products.

This year's UN Climate Conference COP30 in Brazil will become the focus of global attention and is destined to be an important milestone in the global response to climate change, with an impact perhaps no less than the 2015 Paris Climate Conference.

As a veteran participant in the COP conference, Carbonstop will participate in COP for the 14th consecutive year this year (from Doha COP18 in 2012 to Belém COP30 in 2025). From the earliest participants to today's organizers and in-depth observers, we will heavily invite China's leading companies to gather in Brazil, using the United Nations Climate Conference to showcase companies' contributions and innovative practices in carbon reduction and climate change response. We are waiting for you in Brazil!


Tenth Insight: New NDC, New Carbon Reduction Ambition!
The last wave of carbon neutrality was in 2020 and 2021 when the dual carbon goals were proposed, which made the entire industry boil and market sentiment was very high. This year, in 2025, is the fifth anniversary of the dual carbon goals and the tenth anniversary of the Paris Agreement. According to the latest news, China will also update our new NDC, the Nationally Determined Contribution target, around September. Everyone knows that the dual carbon goals in 2020 clarified that China will peak carbon emissions in 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality in 2060, and that carbon emissions per unit of GDP in 2030 will decrease by 65% compared to 2005. Please note that this 65% refers to the decrease in carbon reduction intensity, not the absolute value decrease. Then, the new NDC that China is expected to announce will also clarify China's absolute emission reduction targets, because we will announce the 2035 target, which is after 2030, that is, after the carbon peak, the absolute value needs to decrease. It is expected that this year will be a very important watershed for the carbon neutrality and carbon management industry. The signal for corporate carbon reduction will be clearer, the determination of corporate carbon reduction will be firmer, and the intensity of corporate carbon reduction will reach an unprecedented height. For all of us, whether from government agencies, industry organizations or enterprises, whether in Party A or Party B, this is a rare opportunity for us.
The above are our ten insights into the carbon management industry, and also our thoughts in recent years. Finally, the author wants to say: We can predict the future, we can judge trends; butAction is the only way out!I hope that all of us can take action together, walk side by side, andwelcome the magnificent wave of carbon neutrality together!

